By David Deady
For large companies, recruiting can be expensive, time-consuming, and error-prone. Discovering and attracting the best candidates is challenging, especially in a competitive job market. Onboarding and training are huge costs, not to mention a risky investment if unreliable recruiting processes deliver unsuitable candidates.
Recruiting tools aim to help recruiters manage and streamline attracting, assessing, engaging with, and onboarding new hires. Their goal is to help recruiters be more productive and make it easier to manage hiring for a wide range of roles with a large number of candidates.
In this article, we’ll explore five categories of recruiting tools, explaining how they enhance productivity and cut costs for busy recruiting teams. We’ll also highlight a few of the most widely used and innovative tools in each category.

1. AI Recruitment Tools
Following the introduction of ChatGPT, the fastest-growing web platform of all time, AI tools have been in the spotlight. You may already be using ChatGPT and similar large language model (LLM) platforms to create personalized recruitment emails, write job ads, and summarize and categorize resumes.
But headline-grabbing LLMs like OpenAI’s GPT-4 and Facebook’s LLaMA aren’t the only ones. Many recruiting tools already use AI and machine learning technology to accelerate recruitment, including:
- Celential.ai uses machine learning and natural language processing to source candidates from a large and diverse pool, leveraging AI to identify and score candidates for roles.
- Seekout is a recruiting platform that uses AI-driven search to find the top passive candidates for a particular role. It specializes in identifying hard-to-find candidates with industry-specific capabilities.
- Fetcher streamlines candidate discovery and engagement by leveraging AI to source suitable candidates, send personalized emails, and track and analyze the recruitment pipeline.
2. Recruitment Marketing Platforms
Recruitment marketing platforms (RMPs) are designed to market job listings and help businesses attract suitable candidates. If you’re familiar with marketing automation tools, RMPs will be second nature. They do much the same, except they focus on attracting candidates rather than selling to customers.
An RMP typically has three main functions:
- Marketing and distribution job listings: Promoting job openings across various channels, such as job boards, social media, and search engines, to reach a wider audience.
- Candidate relationship management: Nurturing and engaging with potential candidates by maintaining a talent pipeline, sending personalized messages, and tracking candidate interactions.
- Recruitment analytics: Measuring the effectiveness of recruitment marketing efforts by tracking various metrics, such as the number of applicants, source of applicants, and conversion rates, to optimize strategies and improve future campaigns.
Many RMPs add features like a content management system (CMS) for a recruitment site, systems for managing the candidate experience, and integration with applicant tracking systems (ATS).
Some of the most widely used RMPs include:
- Gusto – a comprehensive payroll and HR solution that includes RMP features such as job and offer management, document management, software provisioning, and onboarding tools.
- Zoho Recruit – which combines ATS, CRM, and RMP features. Its RMP-specific tools include candidate sourcing, job advertising, careers site management, and social recruiting. Zoho Recruit also offers AI “smart” recruitment features to identify and assess quality candidates.
3. Applicant Tracking Systems
Applicant tracking systems (ATS) help organizations manage job postings, collect and organize job applications, screen candidates, schedule interviews, and track the progress of applicants throughout the entire hiring process. An ATS serves as a centralized platform for recruiters and hiring managers, enabling them to efficiently manage multiple job openings and candidates simultaneously.
ATS platforms may include the following features, although each platform has a unique mix of features and integrations with other recruitment tools:
- Job posting management
- Resume and application tracking
- Candidate screening
- Interview scheduling
- Candidate communication
- Reporting and analytics
- Employment compliance management
As you can see, there is some crossover between the features of an RMP and an ATS. Many comprehensive recruitment solutions combine both on a single platform, so it’s always worth taking a look at the features each platform offers.
Among the best-regarded ATS platforms are:
- SmartRecruiters moves beyond just applicant tracking and is an intuitive Talent Acquisition Suite that empowers hiring managers and recruiters to engage and hire candidates. It has full functionality for recruitment marketing and collaborative hiring built on a modern cloud platform.
- Greenhouse, which bills itself as the “hiring operating system for people-first companies.” Its ATS solution offers features to capture and manage candidate information, track applicant data, and automate common recruitment tasks.
- iCIMS ATS, which helps businesses manage the recruiting lifecycle with features that include job advertising, resume screening, interview scheduling, and candidate communication.
- Bullhorn, which is recognized as a “premier provider of CRM and operational software tailored for the staffing sector.” Its ATS platform includes tools for the effective handling of candidate data, optimization of applicant management, and facilitation of essential recruitment tasks, specifically catering to the distinct requirements of staffing firms and recruitment experts.

4. Onboarding and Training Software
Onboarding and training tools help companies bring new employees into their organization and get them up to speed with the company’s culture, policies, and procedures. They can help automate the onboarding and training process, ensuring that new employees have access to the tools and information they need to be successful in their new roles. Onboarding tools have numerous uses, but some of the most valuable are:
- Orientation with role and company processes
- Education regarding company culture and expectations
- Compliance with regulatory and policy requirements
- Tracking onboarding progress and orientation with company processes
Some of the most interesting onboarding and training solutions include:
- Talmudo – an onboarding training platform that offers custom content, scheduled content delivery, and communication tools that connect new hires with peers and managers.
- Eduflow – an interactive training platform that makes it easy for businesses to create engaging and memorable training courses for new hires. It also offers comprehensive training analytics so recruiters can track training progress and the efficacy of their courses.
- Trakstar – which combines many recruitment tools into a single service. We’re highlighting Trakstar Learn, a Learning Management Software (LMS) aimed at helping businesses onboard and train employees in a collaborative learning environment.
5. Learning Experience Platforms for Recruiter Training
In the previous section, we looked at training software for new hires. But what about recruiters themselves? If a company wants to build an effective system for hiring, it needs to invest in the skills and abilities of its recruitment team.
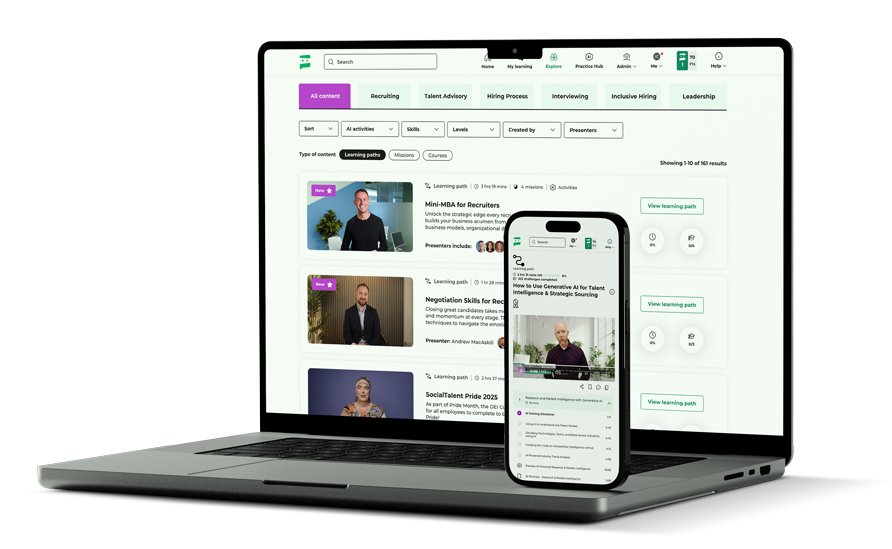
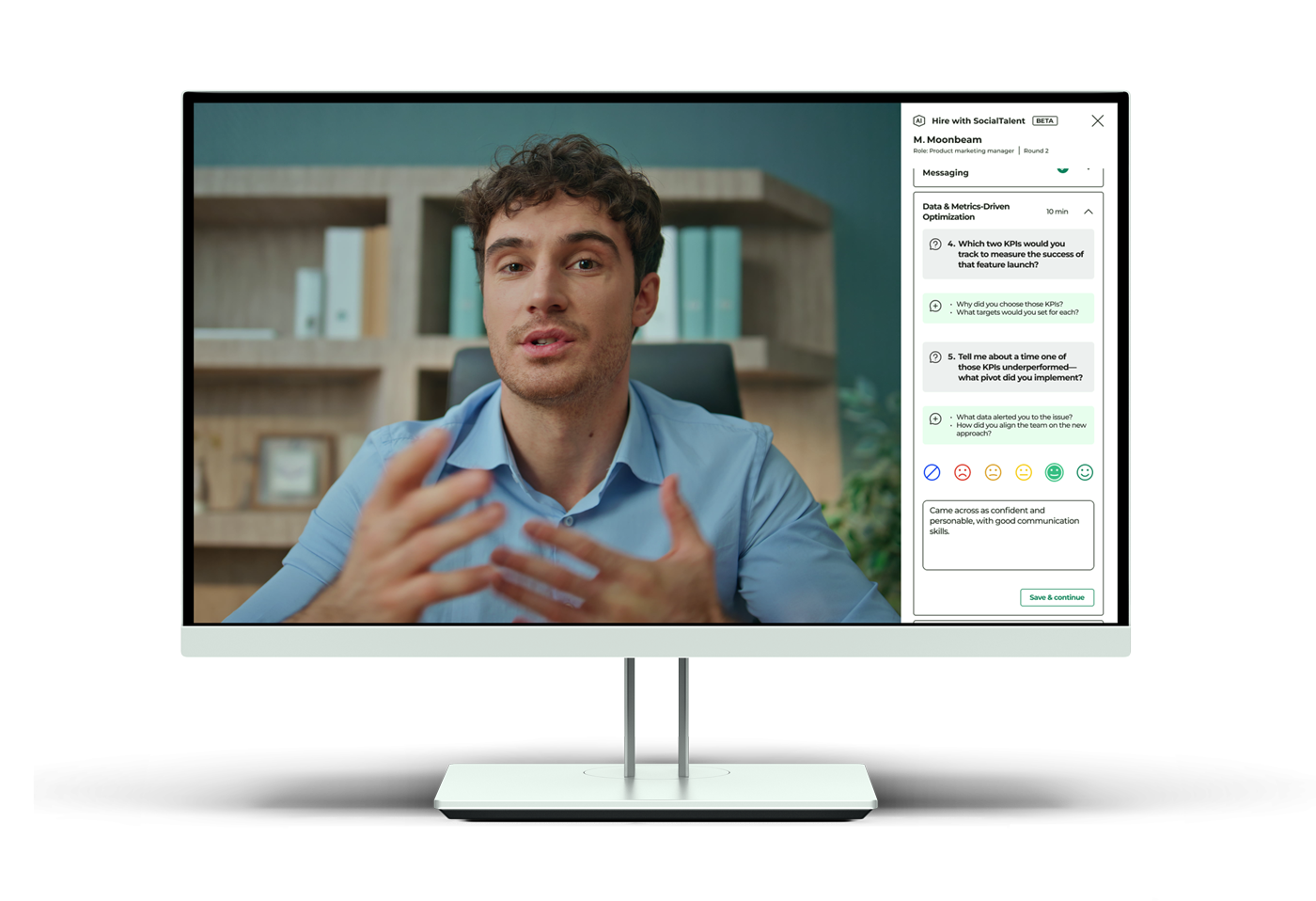
To conclude this article, we’ll look at how you can level up your recruitment team with SocialTalent’s learning experience platform (LXP). LXPs are a more modern alternative to traditional learning management systems (LMS). They provide personalized and user-friendly learning experiences designed to encourage employee engagement.
SocialTalent is an innovative recruiting LXP focused on helping organizations get the most out of their recruitment team and leadership. SocialTalent offers a wide range of training courses for recruiters and hiring managers, including content and educational material focused on: